Understanding Micromanagement in Battle
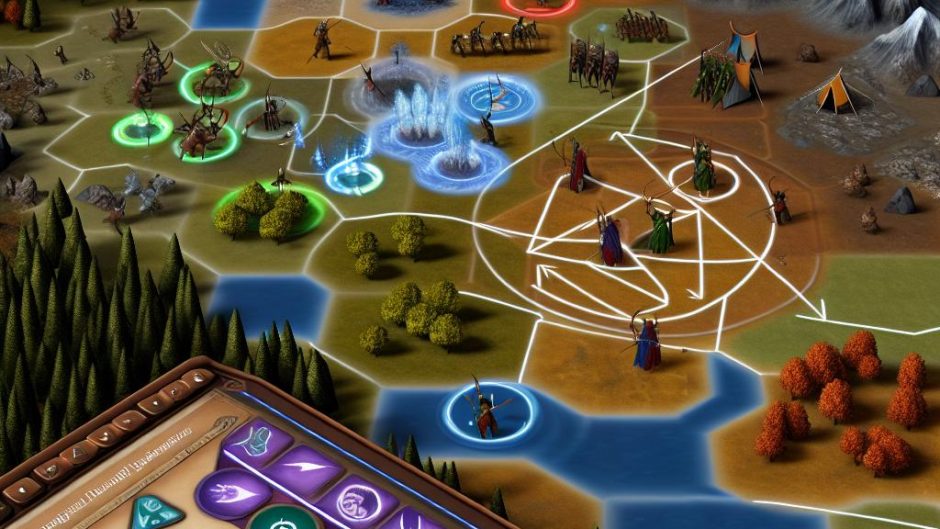
Micromanagement in battles refers to the detailed control and coordination of units to maximize their effectiveness. It plays a crucial role in both real-time and turn-based strategy games, where the player’s ability to manage units directly impacts the outcome of a battle. Effective micromanagement is not just a skill but an art form that provides tactical advantages, enabling players to outmaneuver opponents with superior strategic decisions through precise unit control and coordination.
Analyzing Unit Capabilities
Before engaging in micromanagement, it is imperative to have a comprehensive understanding of the strengths, weaknesses, and special abilities of each unit at your disposal. The effectiveness of micromanagement largely hinges on how adeptly you can exploit these capabilities. In the realm of strategy games, developers often release unit guides or data sheets that offer valuable insights into unit statistics and roles. Analyzing this data enables players to make informed strategic decisions during battles and optimize the potential of each unit.
Positioning and Formation
Strategic positioning and unit formation significantly influence battle outcomes. The placement of units can mean the difference between victory and defeat. For instance, positioning ranged units on elevated terrain can enhance their attack range and visibility, giving them a tactical edge. Meanwhile, placing slower units at the frontline allows them to absorb damage, while faster, more nimble units can maneuver across the battlefield to flank opponents. This tactical positioning minimizes damage and maximizes attacking potential, ensuring that each movement is calculated for maximum impact.
Focus Fire Techniques
An integral part of effective micromanagement is the use of focus fire techniques. This involves concentrating attacks on a single enemy unit, with the goal of quickly eliminating it before moving on to the next target. This strategy proves particularly useful against high-priority threats such as heavily armored units or enemy commanders. Ensuring that your units operate in unison when executing attacks can swiftly deplete enemy forces and mitigate the potential for return damage, often turning the tide of battle in your favor.
Utilizing Special Abilities
Units are often equipped with special abilities that can shift the balance of battle when deployed correctly. These abilities may come with cooldown periods or limited uses, making it vital to deploy them at the most opportune moments. It is essential to familiarize yourself with each unit’s special abilities and to practice using them in various scenarios. Understanding their impact on different enemy types and formations will allow you to deploy these abilities with strategic precision, capitalizing on their potential to surprise and overwhelm the enemy.
Managing Unit Morale and Fatigue
The management of unit morale and fatigue is a critical aspect of maintaining combat effectiveness. Both morale and fatigue can significantly influence performance by affecting factors such as accuracy, speed, and the likelihood of routing from battle. High morale is essential for sustained combat effectiveness and can be maintained by keeping units in proximity to commanding leaders, providing adequate support, and carefully avoiding scenarios where units face overwhelming damage. On the other hand, managing fatigue entails rotating frontline units and allowing them rest periods, especially during protracted engagements, to prevent depletion of their operational capacity.
Effective Use of Hotkeys and Automation
Proficiency in using hotkeys can dramatically enhance the speed and precision of micromanagement. By assigning groups to hotkeys, players can quickly select and issue commands without the need to manually click on each unit, effectively streamlining command execution. Moreover, many strategy games offer various forms of automation, such as configuring unit behaviors or stances. Properly setting up these automated features can reduce the attention needed during chaotic moments and free you up to focus on the broader strategic picture, allowing you to react swiftly and decisively to changing combat conditions.
For those seeking to further refine their micromanagement skills, engaging with gaming communities and delving into strategy guides can provide a treasure trove of advanced techniques tailored to different games. Many forums and guides discuss micromanagement in depth, providing practical tips and insights that can enhance your understanding of micromanagement tactics. Engaging with these resources can expand your strategic repertoire and deepen your expertise, enabling you to face any battle scenario with increased confidence and competence. Visit a strategy forum to learn more about these techniques and connect with fellow enthusiasts who share your passion for strategic gameplay.










Recent Comments